In chromatography, there is a division of a substance between two phases. These are called the stationary phase (a solid liquid or liquid attached to a support material) and mobile phase (the gas or liquid that moves along the stationary phase). The partition coefficient is the distribution of a substance between these two phases.
Chromatography comes in two forms: liquid chromatography and gas chromatography.
Liquid and Gas Chromatography systems
Liquid chromatography uses liquid as the mobile phase, also called eluent.
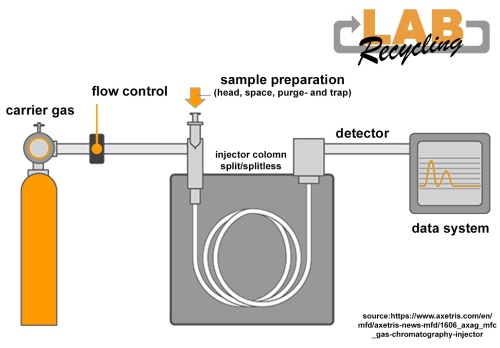
In gas chromatography, carrier gas is used as the mobile phase. With a gas chromatograph, chromatography is only used with gas.
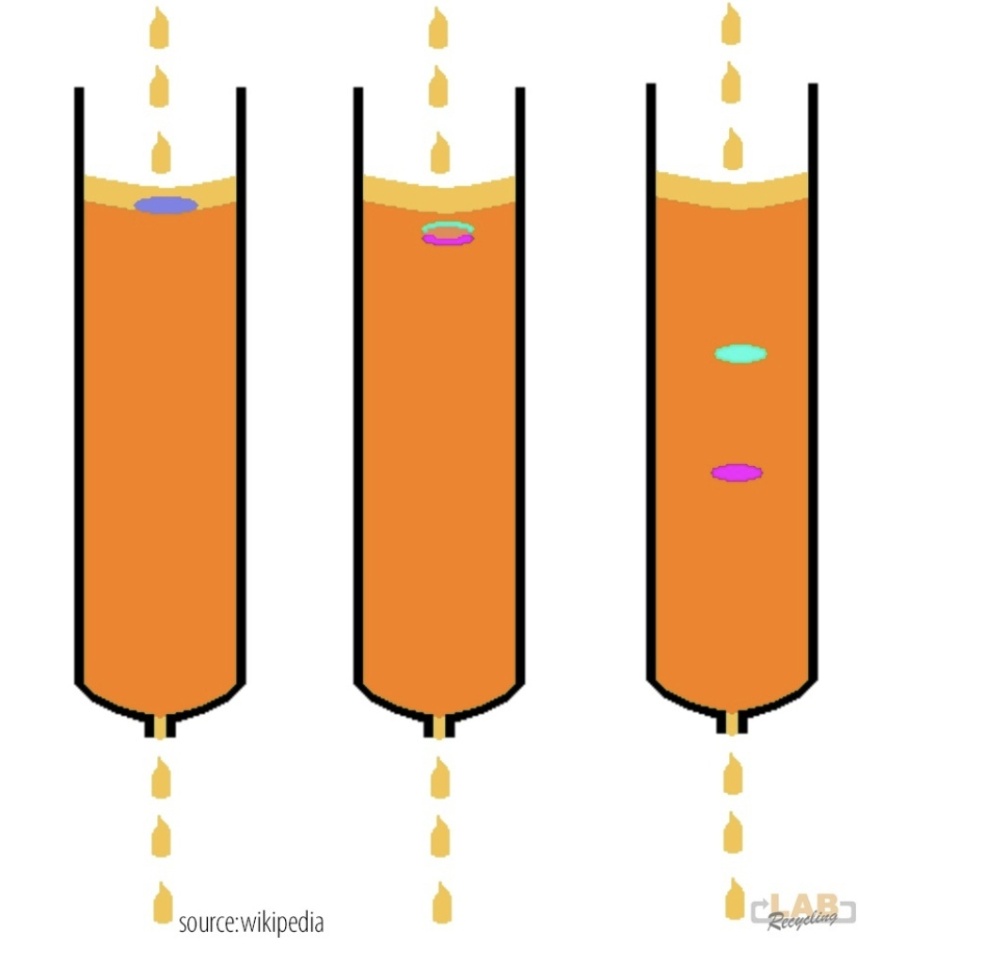
The three columns below show the separation principle. The system consists of a column filled with a solid stationary phase (purple/blue) through which a liquid mobile phase flows (orange). When a mixture of two substances (blue and pink) is applied to the column, both substances are transported through the column, but because the yellow substance adheres more strongly to the stationary phase than the red substance, the two substances leave the column one by one. The mixture is thus separated.
The three columns below show the separation principle. The system consists of a column filled with a solid stationary phase (purple/blue) through which a liquid mobile phase flows (orange). When a mixture of two substances (blue and pink) is applied to the column, both substances are transported through the column, but because the yellow substance adheres more strongly to the stationary phase than the red substance, the two substances leave the column one by one. The mixture is thus separated.
With the use of chromatography equipment in laboratories, substances are separated from each other. This equipment can be divided into the following 6 groups:
GC systems
HPLC sytems
GC/MS systems
LC/MS systems
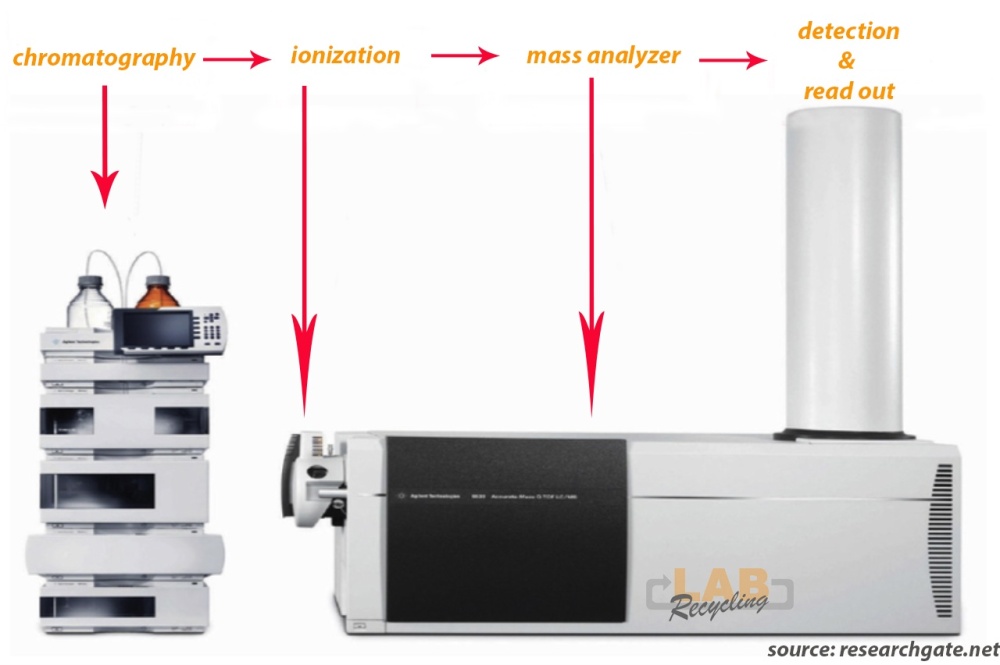
A LC/MS system is a combination of a UHPLC system or HPLC with a MS (mass spectrometer system).
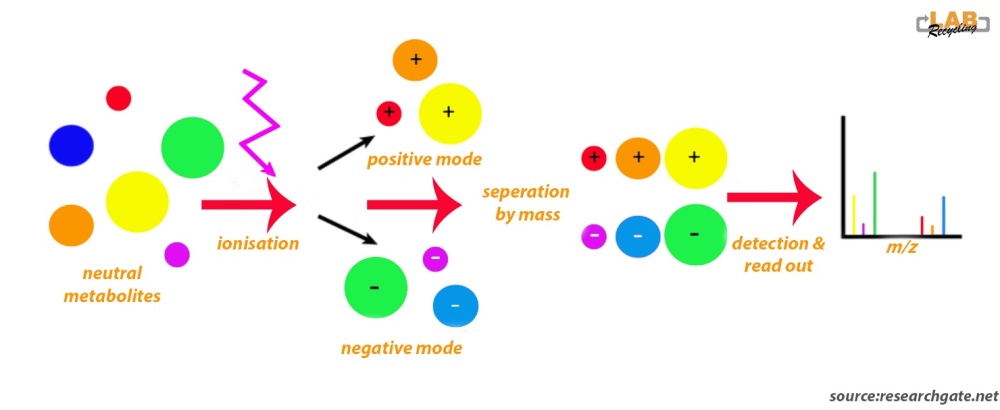
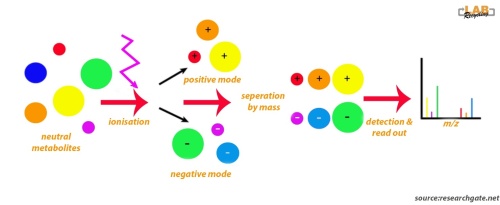
The picture below shows an analytical workflow of liquid chromatography (LC)-mass spectroscopy (MS. The illustration shows that neutral molecules are ionisated with an electrospray. Following ionization, negatively and positively charged compounds are generated. LC-MS conducted in negative and positive modes will detect negatively and positively charged ions, respectively.
Complex equipment is needed to conduct LC-MS metabolomics. The first step is chromatography followed by ionization and mass analysis of the molecules.
AAS systems
What are AAS systems
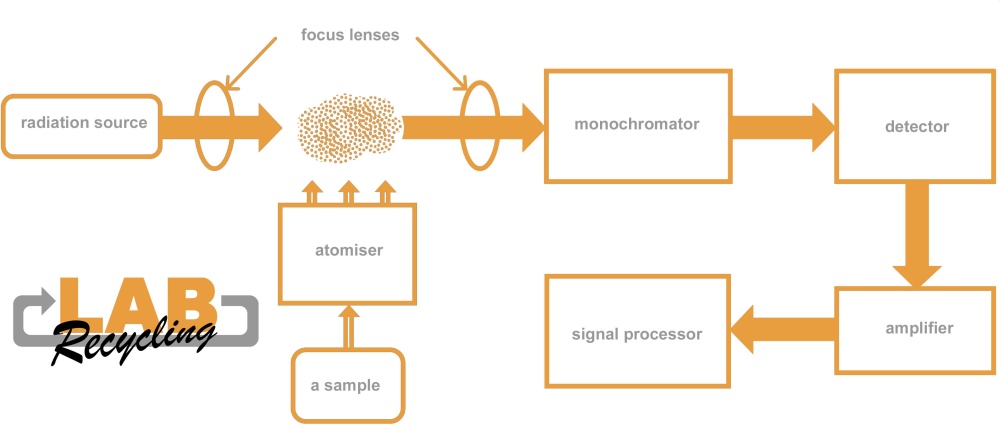
Atomic absorption spectrometry is an analytical technique using selective absorption of electromagnetic radiation by atoms. A sample is pulverised in a flame. A lamp is then used to emit light into the flame. The emitted light is absorbed by the atoms in the flame. The degree of absorption is determined by the concentration of atoms in the flame and therefore also by the concentration of atoms in the sample.
With this analysis technique, metal atoms are measured. The size in which metals can be measured is in the order of ppm, i.e. mg/l or μg/ml.